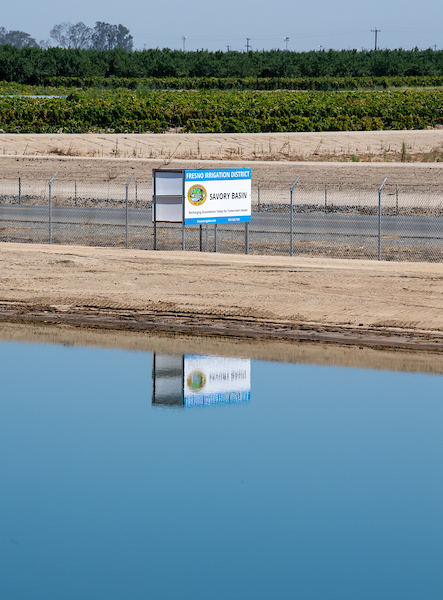
It was exactly the sort of deluge California groundwater agencies have been counting on to replenish their overworked aquifers.
The start of 2023 brought a parade of torrential Pacific storms to bone dry California. Snow piled up across the Sierra Nevada at a near-record pace while runoff from the foothills gushed into the Central Valley, swelling rivers over their banks and filling seasonal creeks for the first time in half a decade.
Suddenly, water managers and farmers toiling in one of the state’s most groundwater-depleted regions had an opportunity to capture stormwater and bank it underground. Enterprising agencies diverted water from rushing rivers and creeks into manmade recharge basins or intentionally flooded orchards and farmland. Others snagged temporary permits from the state to pull from streams they ordinarily couldn’t touch.
Yet not everyone was able to fully capitalize on Mother Nature’s gift.